- Anti-hestaminic & Respiratory Drugs (20)
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs (197) +-
- Baby & Mom (1346) +-
- Baby & Mom > Bath, skin & Hair > Skin Care > wibes (52)
- Beauty (3129) +-
- Beauty > Skin Care > whitening (309)
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response (885) +-
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response > ANTI-FUNGAL (11)
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response > Chemotherapeutic Agents > Hormone Antagonists >Enzyme Inhibitors (290)
- CIRCULATORY DISTURBANCE AGENTS (24)
- Diet & Fitness Products (284) +-
- DRUG AFFECTING CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (191)
- HEMATOLOGY (39)
-
Medical Supplies (506)
+-
- Chemicals & Disinfectants (19)
- Dental Supplies (31)
- Devices & Instruments (11)
- Diabetic Supplies (121)
- General Medical Supplies (21)
- I.V & Medical Solution (0)
- Intensive Care Unit & Anesthesia Supplies (0)
- KIDNEY UNIT SUPPLIES (21)
- Lab Supplies (3)
- Miscellaneous (21)
- Neonatal Unit Supplies (0)
- Operation Room Supplies (2)
- Sanitary (5)
- Sterilization Supplies (1)
- Surgical Sutures (4)
- Syringes (3)
-
Medicines & Health (2727)
+-
- Allergy & Sinus (97)
- Children's Health Care (54)
- Cough, Cold & Flu (283)
- Digestive Health & Nausea (231)
- Ear, Nose & Throat Care (181)
- Eye Care (124)
- Feminine Care (323)
- Foot Care (12)
- Orthopaedic Appliances (1)
- Pain Relief & Management (244)
- Pill Organizer (2)
- Skin Treatments (863)
- Sleep & Snoring Aids (2)
- Support & Braces (8)
- Medicines & health > Gout releif (42)
- Natural & Organic Products (81) +-
- OTC > Analgesics > Anti-inflammatory Drugs (44)
-
Personal Care (3363)
+-
- Bath & Body (273)
- Deodorant & Anti-perspirants (191)
- Ear, Nose & Throat Care (177)
- Eye Care (131)
- Feminine Care (372)
- Foot Care (20)
- Hair Care (511)
- Home Tests & Monitorings (14)
- Incontinence (7)
- Lip Care (26)
- Massage & Relaxation (17)
- Natural & Organic Personal Care (7)
- Oral Care (91)
- Pregnancy & Fertility (64)
- Shaving & Grooming (75)
- Sun Care (80)
-
Prescription Drugs (2935)
+-
- Analgesics (184)
- Cardiovascular System (377)
- Drugs Affecting Musculoskeletal System (65)
- Drugs Used In Infections (56)
- Ear & Nose Drugs (2)
- Endocrine System (177)
- Gastrointestinal Tract (243)
- Gastrointestinal Tract > Hepatology > Liver treatment (60)
- GYNECOLOGY (2)
- Miscellaneous (11)
- NEPHROLOGY > URINARY SYSTEM > RENAL DISORDERS > URINARY TRACT DISORDERS (47)
- NEUROLOGY (228)
- Nutrients & Blood Electrolytes (2)
- Respiratory System (154)
- SKIN > NAILS > HAIR > TOPICAL PREPARATIONS (115)
- Vaccines (1)
- Prescription drugs > Cardiovascular system > Anti-hypertension drugs (242)
- Sexual Wellness (304) +-
- Vitamins & Minerals Supplements (1232) +-
Ex Tax: 13,597EGP
Example
You can return the product within 14 days of purchase.
ReturnsYou can return the product within 14 days of purchase.

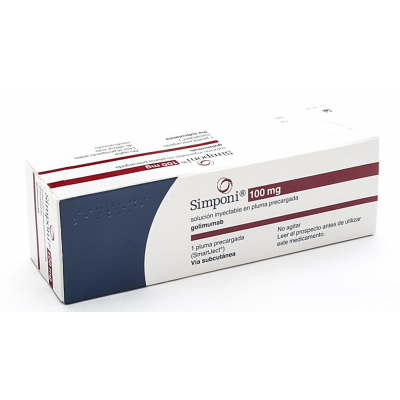
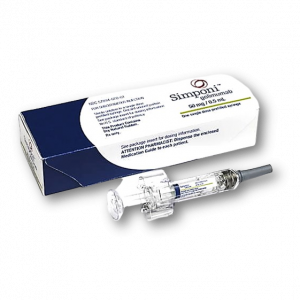
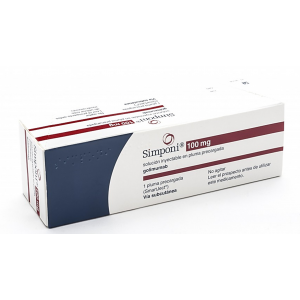
Simponi ® 100 mg ( golimumab ) solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
SERIOUS INFECTIONS
SIMPONI® (golimumab) is a prescription medicine. SIMPONI® can lower your ability to fight infections. There are reports of serious infections caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses that have spread throughout the body, including tuberculosis (TB) and histoplasmosis. Some of these infections have been fatal. Your doctor will test you for TB before starting SIMPONI® and will monitor you for signs of TB during treatment. Tell your doctor if you have been in close contact with people with TB. Tell your doctor if you have been in a region (such as the Ohio and Mississippi River Valleys and the Southwest) where certain fungal infections like histoplasmosis or coccidioidomycosis are common.
You should not start SIMPONI® if you have any kind of infection. Tell your doctor if you are prone to or have a history of infections or have diabetes, HIV or a weak immune system. You should also tell your doctor if you are currently being treated for an infection or if you have or develop any signs of an infection such as:
- fever, sweat, or chills
- muscle aches
- cough
- shortness of breath
- blood in phlegm
- weight loss
- warm, red, or painful skin or sores on your body
- diarrhea or stomach pain
- burning when you urinate or urinate more than normal
- feel very tired
Your doctor will examine you for TB and perform a test to see if you have TB. If your doctor feels that you are at risk for TB, you may be treated with medicine for TB before you begin treatment with SIMPONI® and during treatment with SIMPONI®. Even if your TB test is negative, your doctor should carefully monitor you for TB infections while you are taking SIMPONI®. People who had a negative TB skin test before receiving SIMPONI® have developed active TB. Tell your doctor if you have any of the following symptoms while taking or after taking SIMPONI®:
- cough that does not go away
- low grade fever
- weight loss
- loss of body fat and muscle (wasting)
Cancer
Unusual cancers have been reported in children and teenage patients taking TNF-blocker medicines. For children and adults taking TNF blockers, including SIMPONI®, the chances for getting lymphoma or other cancers may increase. Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma, a rare and fatal lymphoma, has occurred mostly in teenage or young adult males with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis who were taking other TNF blockers with azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine. You should tell your doctor if you have had or develop lymphoma or other cancers.
Some people treated with SIMPONI® have developed certain kinds of skin cancer. If any changes in the appearance of your skin or growths on your skin occur during or after your treatment with SIMPONI®, tell your doctor.
USE WITH OTHER DRUGS
Tell your doctor about all the medications you take including ORENCIA® (abatacept), KINERET® (anakinra), ACTEMRA® (tocilizumab), RITUXAN® (rituximab), or another TNF blocker, or if you are scheduled to or recently received a vaccine. People taking SIMPONI® should not receive live vaccines or treatment with a weakened bacteria (such as BCG for bladder cancer).
HEPATITIS B INFECTION
Reactivation of hepatitis B virus has been reported in patients who are carriers of this virus and are taking TNF-blocker medicines, such as SIMPONI®. Some of these cases have been fatal. Your doctor should do blood tests before and after you start treatment with SIMPONI®. Tell your doctor if you know or think you may be a carrier of hepatitis B virus or if you experience signs of hepatitis B infection, such as:
- feel very tired
- dark urine
- skin or eyes look yellow
- little or no appetite
- vomiting
- muscle aches
- clay-colored bowel movements
- fevers
- chills
- stomach discomfort
- skin rash
HEART FAILURE
Heart failure can occur or get worse in people who use TNF blockers, including SIMPONI®. If you develop new or worsening heart failure with SIMPONI®, you may need treatment in a hospital, and it may result in death. Your doctor will closely monitor you if you have heart failure. Tell your doctor right away if you get new or worsening symptoms of heart failure like shortness of breath, swelling of your lower legs or feet, or sudden weight gain.
NERVOUS SYSTEM PROBLEMS
Rarely, people using TNF blockers, including SIMPONI®, can have nervous system problems such as multiple sclerosis or Guillain-Barré syndrome. Tell your doctor right away if you have symptoms like vision changes, weakness in your arms or legs, or numbness or tingling in any part of your body.
IMMUNE SYSTEM PROBLEMS
Rarely, people using TNF blockers have developed lupus-like symptoms. Tell your doctor if you have any symptoms such as a rash on your cheeks or other parts of the body, sensitivity to the sun, new joint or muscle pain, becoming very tired, chest pain or shortness of breath, swelling of the feet, ankles, and/or legs.
LIVER PROBLEMS
Serious liver problems can happen in people using TNF blockers, including SIMPONI®. Contact your doctor immediately if you develop symptoms such as feeling very tired, skin or eyes look yellow, poor appetite or vomiting, or pain on the right side of your stomach.
BLOOD PROBLEMS
Low blood counts have been seen with SIMPONI®. If this occurs, your body may not make enough blood cells to help fight infections or help stop bleeding. Your doctor will check your blood counts before and during treatment. Tell your doctor if you have signs such as fever, bruising, bleeding easily, or paleness.
OTHER CONSIDERATIONS TO TELL YOUR DOCTOR
Tell your doctor if you are allergic to rubber or latex. The needle cover contains dry natural rubber.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant or are breastfeeding or have a baby and were using SIMPONI® during pregnancy. Tell your baby’s doctor before your baby receives any vaccine because of an increased risk of infection for up to 6 months after birth.
ALLERGIC REACTIONS
Allergic reactions can happen in people who use TNF-blocker medicines, including SIMPONI®. Tell your doctor if you have any symptoms of an allergic reaction while taking SIMPONI® such as hives, swollen face, breathing trouble, or chest pain. Some reactions can be serious and life-threatening.
Common side effects of SIMPONI® include: upper respiratory tract infection, reaction at site of injection, and viral infections.
PSORIASIS
New or worse psoriasis symptoms may occur. Tell your doctor if you develop red scaly patches or raised bumps that are filled with pus.
Please read the full Prescribing Information and Medication Guide for SIMPONI® and discuss any questions you have with your doctor.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch, or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
INDICATIONS AND DOSING
SIMPONI® is a prescription medicine for adults with:
- Moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA), with the medicine methotrexate (MTX)
- Active psoriatic arthritis (PsA), alone or with the medicine MTX
- Active ankylosing spondylitis (AS)
- Moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) when certain other UC medicines have not worked well enough or cannot be tolerated, or if it is necessary to continue taking steroid medicines:
- To begin helping some of your symptoms
- In people who respond to SIMPONI®, to get their UC under control (induce remission) and keep UC under control (sustain remission)
- To begin to improve the way the lining of your large intestine looks to your doctor during colonoscopy
MTX is used as directed.
For RA, PsA, and AS: SIMPONI® 50 mg is given as an injection under the skin (subcutaneous injection) once a month.
For UC: SIMPONI® begins with 3 starter injections under the skin (subcutaneous injection): Two 100-mg injections on the first day of treatment, followed by one 100-mg injection 2 weeks later. After these 3 starter injections, SIMPONI® requires one 100-mg injection every 4 weeks.
Once you and your doctor are comfortable with the self-injection process, you will inject SIMPONI® under the skin.
Write a review
Your Name:Your Review: Note: HTML is not translated!
Rating: Bad Good
Enter the code in the box below: