- Anti-hestaminic & Respiratory Drugs (20)
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs (192) +-
- Baby & Mom (1314) +-
- Baby & Mom > Bath, skin & Hair > Skin Care > wibes (52)
- Beauty (2883) +-
- Beauty > Skin Care > whitening (276)
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response (882) +-
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response > ANTI-FUNGAL (11)
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response > Chemotherapeutic Agents > Hormone Antagonists >Enzyme Inhibitors (289)
- CIRCULATORY DISTURBANCE AGENTS (24)
- Diet & Fitness Products (280) +-
- DRUG AFFECTING CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (191)
- HEMATOLOGY (39)
-
Medical Supplies (504)
+-
- Chemicals & Disinfectants (19)
- Dental Supplies (32)
- Devices & Instruments (10)
- Diabetic Supplies (121)
- General Medical Supplies (21)
- I.V & Medical Solution (0)
- Intensive Care Unit & Anesthesia Supplies (0)
- KIDNEY UNIT SUPPLIES (21)
- Lab Supplies (3)
- Miscellaneous (21)
- Neonatal Unit Supplies (0)
- Operation Room Supplies (2)
- Sanitary (5)
- Sterilization Supplies (0)
- Surgical Sutures (4)
- Syringes (3)
-
Medicines & Health (2602)
+-
- Allergy & Sinus (95)
- Children's Health Care (54)
- Cough, Cold & Flu (277)
- Digestive Health & Nausea (225)
- Ear, Nose & Throat Care (179)
- Eye Care (117)
- Feminine Care (321)
- Foot Care (4)
- Orthopaedic Appliances (0)
- Pain Relief & Management (237)
- Pill Organizer (2)
- Skin Treatments (785)
- Sleep & Snoring Aids (2)
- Support & Braces (7)
- Medicines & health > Gout releif (42)
- Natural & Organic Products (81) +-
- OTC > Analgesics > Anti-inflammatory Drugs (44)
-
Personal Care (3169)
+-
- Bath & Body (261)
- Deodorant & Anti-perspirants (182)
- Ear, Nose & Throat Care (175)
- Eye Care (123)
- Feminine Care (370)
- Foot Care (12)
- Hair Care (448)
- Home Tests & Monitorings (14)
- Incontinence (7)
- Lip Care (22)
- Massage & Relaxation (17)
- Natural & Organic Personal Care (7)
- Oral Care (89)
- Pregnancy & Fertility (64)
- Shaving & Grooming (65)
- Sun Care (78)
-
Prescription Drugs (2870)
+-
- Analgesics (181)
- Cardiovascular System (374)
- Drugs Affecting Musculoskeletal System (65)
- Drugs Used In Infections (56)
- Ear & Nose Drugs (2)
- Endocrine System (176)
- Gastrointestinal Tract (242)
- Gastrointestinal Tract > Hepatology > Liver treatment (61)
- GYNECOLOGY (2)
- Miscellaneous (11)
- NEPHROLOGY > URINARY SYSTEM > RENAL DISORDERS > URINARY TRACT DISORDERS (46)
- NEUROLOGY (222)
- Nutrients & Blood Electrolytes (2)
- Respiratory System (154)
- SKIN > NAILS > HAIR > TOPICAL PREPARATIONS (68)
- Vaccines (1)
- Prescription drugs > Cardiovascular system > Anti-hypertension drugs (242)
- Sexual Wellness (297) +-
- Vitamins & Minerals Supplements (1195) +-
Ex Tax: 50EGP
Example
You can return the product within 14 days of purchase.
ReturnsYou can return the product within 14 days of purchase.

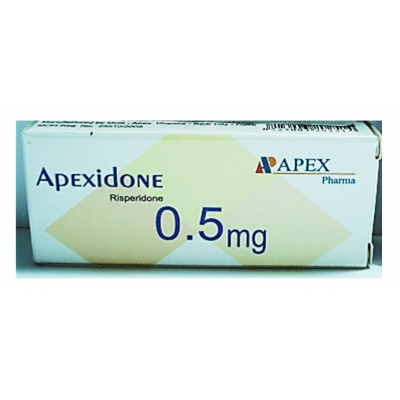
Apexidone 0.5 mg ( Risperidone ) 30 film-coated tablets
How to take Apexidone?
Your dose and how often you take Apexidone will depend on the following factors:
age
weight
patient's health
the health of the patient's liver
the health of the patient's kidneys
response to the medicine
Apexidone Dosage
Dosage for severe mental disorder (schizophrenia)
Adult
Recommended: 1-2 mg/day oral dose added after 24 hours of initial dose up to 4-8 mg/day based on patient's response or 25 mg intramuscular injection every 2 weeks
Initial: 2 mg/day orally in one or two divided doses
Maximum: 16 mg/day orally or 50 mg intramuscular injection every 2 weeks
Children
Recommended: 0.5-1 mg/day oral dose added after 24 hours of initial dose up to 3 mg/day based on patient's response
Initial: 0.5 mg once daily orally
Maximum: 6 mg/day orally
Older Adults
Recommended: 0.5 mg twice daily dose added to initial dose up to 1-2 mg twice daily based on patient's response
Initial: 0.5 mg tablet twice daily
Dosage for periods of abnormally elevated mood (bipolar mania)
Adult
Recommended: 1 mg/day oral dose added or decreased after 24 hours of initial dose up to 1-6 mg/day based on patient's response
Initial: 2-3 mg/day orally once daily
Maximum: 6 mg/day orally
Children
Recommended: 0.5 mg or 1 mg/day oral dose added after 24 hours of initial dose up to 2.5 mg/day based on patient's response
Initial: 0.5 mg once daily orally
Older Adults
Recommended: 0.5 mg twice daily dose added to initial dose up to 1-2 mg twice daily based on patient's response
Initial: 0.5 mg tablet twice daily
Dosage for periods of depression and abnormally elevated mood (bipolar I disorder)
Adult
Recommended: 25 mg intramuscular injection every 2 weeks
Maximum: 50 mg intramuscular injection every 2 weeks
Dosage for irritability associated with inability to communicate and interact (autistic disorder)
Children (weighing less than 20 kg or 44.1 lb)
Recommended: 0.5 mg/day orally after 4 days of initial dose and in patients unresponsive to this dose after 14 days add an increment of 0.25 mg/day
Initial: 0.25 mg/day orally once daily
Children (weighing equal to or more than 20 kg or 44.1 lb)
Recommended: 1 mg/day orally after 4 days of initial dose and in patients unresponsive to this dose after 14 days add an increment of 0.5 mg/day
Initial: 0.5 mg/day orally once daily
Dosage for persistent aggression in patients with moderate to severe memory loss
Adult
Recommended: 0.25 mg tablet twice daily may be added to the starting dose every other day. In some patients, 0.5 or 1 mg tablet twice daily may benefit.
Initial: 0.25 mg twice daily tablet
Dosage for persistent aggression with antisocial behaviour (conduct disorder)
Children (aged 5 to 18 years with weight equal to or more than 50 kg or 110.2 lb)
Recommended: 0.5 mg tablet once daily may be added to the starting dose every other day. In some patients, 1 or 1.5 mg tablet once daily may benefit.
Initial: 0.5 mg once daily tablet
Children (aged 5 to 18 years with weight less than 50 kg or 110.2 lb)
Recommended: 0.25 mg tablet once daily may be added to the starting dose every other day. In some patients, 0.25, 0.5 or 0.75 mg tablet once daily may benefit.
Initial: 0.25 mg once daily tablet
Minimum Age
5 years
Dosage calculation for children
To calculate the dosage for children please use the weight based dose calculator to calculate the appropriate dosage as per the weight of your child.
Forms
Tablet
Strength: 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, 4 mg and 5 mg
Orally Disintegrating Tablets
Strength: 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg
Solution
Strength: 1 mg/ml
Powder for Suspension, Extended Release Injection
Strength: 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg, and 50 mg
Film-Coated Tablets
Strength: 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, 4 mg, and 6 mg
Coated Tablets
Strength: 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg
Special Instructions
Elderly or weaken patients
The recommended oral dose of Apexidone is 0.5 mg twice daily and it should not be increased more than 0.5 mg twice daily. After one week, the dose may be increased above 1.5 mg twice daily. For Apexidone injection, the recommended dose is 25 mg every two weeks. Along with the first injection, give oral Apexidone and continue for three weeks.
Kidney or liver dysfunction
The recommended dose of Apexidone should be 0.5 mg twice daily orally for the first week, can be increased for the second week to 1 mg twice or 2 mg once daily. If the daily dose of 2 mg is well tolerated, 25 mg injection of Apexidone can be given every 2 weeks. After the first injection, oral dose of Apexidone should be continued for three weeks.
Patients at risk of low blood pressure
The recommended oral dose of Apexidone is 0.5 mg twice daily and it should not be increased more than 0.5 mg twice daily. After one week, the dose may be increased above 1.5 mg twice daily.
Patients having a history of poor tolerability with psychotropic medicines
12.5 mg starting dose of Apexidone should be given to such patients. The efficacy study of 12.5 mg dose has not been established in clinical trials.
Missed Dose
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it's time for the next dose. Do not take a double dose to make up for the dose that you may have missed.
Overdose
What to do if you overdose on Apexidone?
In case of overdose, oxygen or artificial respiration should be given for breathing problems. Stomach emptying and use of charcoal, a substance that absorbs poisons from the stomach should be done along with stool softeners. Carefully monitor heart and vital signs and also provide supportive care for low blood pressure and failure of blood circulation. Anticholinergic drugs should be given for severe extrapyramidal symptoms. Close monitoring continued until patient recovers.
Symptoms of an overdose of Apexidone
If you use too much of this medicine, it could lead to dangerous levels of the medicine in your body. In such cases, symptoms of an overdose may include:
abnormally fast heart rhythm
drowsiness
extrapyramidal symptoms such as involuntary muscle contractions, motor restlessness, rigidity, slow movement, tremor, irregular body movements
increased heartbeat
low blood potassium level
low blood pressure
low blood sodium level
prolonged heartbeat
seizures
sleepiness
If you think you have overdosed on Apexidone Tablet, call a poison control center immediately. You can look up the poison control center information from the Poison Center Finder at TabletWise.com.
Precautions while using Apexidone
Before you use Apexidone Tablet, tell your doctor if you are allergic to it or its ingredients. Your doctor may prescribe an alternative medicine and update your medical records to record this information.
Before you use Apexidone, tell your doctor of your medical history including heart problem, drug-induced low level of white blood cells (leukopenia/neutropenia), seizures, drug abuse, diabetes, progressive neurological disorder (Parkinson’s disease), dementia, epilepsy, kidney problems, liver problems, an abnormally high level of the hormone prolactin, family history of blood clots, uncontrolled movement of the mouth, tongue, and face, high temperature, muscle stiffness, sweating, a lowered level of consciousness, prolonged or painful erection, heart problem, drug-induced low level of white blood cells (leukopenia/neutropenia), seizures, drug abuse, diabetes, progressive neurological disorder (Parkinson’s disease), dementia, epilepsy, kidney problems, liver problems, an abnormally high level of the hormone prolactin, family history of blood clots, uncontrolled movement of the mouth, tongue, and face, high temperature, muscle stiffness, sweating, a lowered level of consciousness, prolonged or painful erection, heart attack, heart failure, heart rhythm abnormalities (conduction abnormalities), disease of blood vessels in the brain (cerebrovascular disease), dehydration, decreased blood volume (hypovolemia), or poor tolerability to the medicines that affects the mind. A low dose of Apexidone is used in these patients and caution is advised. Before having any surgery when using Apexidone, tell your doctor and dentist about all the medicinal products you use including prescription and non-prescription medicines, and any herbal supplements.
The use of this medicine may change glucose levels. The diabetic patient should undergo fasting glucose testing at the starting of the treatment and frequently during the therapy. All patients receiving Apexidone should be observed for the symptoms of high blood glucose.
The use of Apexidone Tablet may change white blood cell count. Apexidone may cause a low level of white blood cells. Patients with the history of a low white blood cell count and drug-induced low white blood cell count should have their complete blood count (CBC). Regularly monitor CBC throughout the first few months of the treatment. Discontinuation of the therapy should be considered if there is a sign of a decline in white blood cell count.
The use of this medicine may change the prolactin level. This medicine may increase the level of prolactin hormone. Due to this, a milky discharge from the breast (galactorrhea), an absence of menstruation (amenorrhea), enlarged breasts in men (gynecomastia), and difficulty in erection (impotence) can occur. Long-standing high level of prolactin in the blood (hyperprolactinemia) when associated with abnormally low levels of the sex hormones (hypogonadism) may results in decreased bone density in both male and female.
Avoid the consumption of alcohol with Apexidone Tablet.
Apexidone Tablet should be used in pregnancy only when required. There are increased chances of side-effects in the babies if antipsychotics are used in the third trimester. This may include withdrawal symptoms or extrapyramidal symptoms such as muscle contractions, motor restlessness, rigidity, slowness of movement, tremor and irregular jerky movements. There are some reports of nervousness (agitation), low muscle tone (hypotonia), increased muscle tone (hypertonia), tremor, respiratory distress, sleepiness, or feeding disorder. As a result, the baby should be monitored carefully. Apexidone Tablet is not safe for use in women who are breastfeeding. If you are breastfeeding, discuss with your doctor if you should either discontinue breastfeeding or stop using this medicine while breastfeeding. This medicine may pass into breast milk. Consult with your doctor on the use of Apexidone Tablet, if you are trying to conceive.
Apexidone Tablet can make you feel sleepy. Be careful while driving, using machinery, or doing any other activity that needs you to be alert. The consumption of alcohol with Apexidone Tablet can make you feel more sleepy. Apexidone Tablet may cause seizures in some people. Discuss with your doctor if you perform activities where a loss of consciousness may cause you or others harm.
Apexidone can increase your risk of getting infections/worsen existing infections. Reduce your chances of new infections. Wash your hands often. Avoid people who may have infectious diseases. Prevent injuries, cuts, and bruises. Do not vaccinate without discussing with your doctor. Apexidone may increase the risk of infections such as common cold, flu, inflammation of the lung airways, urinary tract infection, stuffy nose, pneumonia, ear infection, lower respiratory tract infection, inflammation of the pharynx or viral infection, and abscess under the skin (subcutaneous abscess).
Apexidone Tablet may cause an increased risk of side-effects in younger patients. Children using this medicine may see an increased risk of sleepiness, fatigue, headache, increased appetite, vomiting, upper respiratory tract infection, nasal congestion, stomach pain (abdominal pain), dizziness, cough, fever, tremor, diarrhea, and involuntary urination (enuresis).
Apexidone Tablet may increase side-effects in older patients. Elderly patients may see an increased risk of mini-stroke (transient ischaemic attack), stroke (cerebrovascular accident), urinary tract infection, swelling of the legs, lack of energy (lethargy), and cough.
Apexidone Side-effects
The following side-effects may commonly occur when using Apexidone Tablet. If any of these side-effects worsen or last for a long time, you should consult with your doctor:
abnormal movements of the mouth, eyes, tongue or jaw (dystonia)
anxiety
back pain
blurry vision
chest pain
common cold symptoms
constipation
cough
decreased appetite
depression
diarrhea
dizziness
drowsiness
dry mouth
ear infection (otitis media)
eye infection (conjunctivitis)
fall
fatigue
feeling like flu (influenza-like symptoms)
fever
headache
high blood pressure
increased appetite
increased level of prolactin hormone (hyperprolactinemia)
increased saliva
indigestion (dyspepsia)
infection of the chest (bronchitis)
insomnia
involuntary muscle movements (dyskinesia)
irritability
joint pain (arthralgia)
lack of control of urine (incontinence)
movement disorder due to inner restlessness feeling and an urge to move
muscle pain
muscle spasms
nausea
nose bleeds
parkinsonism
pneumonia
rapid heart rate
rash
shortness of breath
sinus infection
skin redness
sore throat
stomach discomfort (abdominal discomfort)
stomach pain (abdominal pain)
stuffy nose (rhinitis)
swelling of the body, arms or legs
toothache
tremor
upper respiratory tract infection
urinary tract infection
vomiting
weakness
weight gain
The following side-effects may commonly occur in older patients on the use of Apexidone Tablet. Discuss with your doctor if any of these side-effects last for a long time or are severe:
cough
lethargy
mini stroke (transient ischaemic attack)
stroke (cerebrovascular accident)
swelling of the lower limbs caused by an accumulation of fluid
urinary tract infection
The following side-effects may commonly occur in children when using Apexidone Tablet. Discuss with your doctor if any of these side-effects last for a long time or are severe:
abnormal vision
anxiety
confusion
constipation
cough
diarrhea
dizziness
drowsiness
dry mouth
fatigue
fever
headache
increased appetite
increased heartbeat
increased saliva
increased weight
indigestion (dyspepsia)
involuntary muscle contractions (dystonia)
involuntary muscle movements (dyskinesia)
involuntary urination (enuresis)
leakage of milk from the breasts (lactation nonpuerperal)
loss of appetite resulting in malnutrition and low body weight (anorexia)
movement disorder due to inner restlessness feeling and an urge to move
nasal congestion
nausea
progressive neurological disorder (Parkinson disorder)
rash
shortness of breath (dyspnea)
stomach pain (abdominal pain)
stuffy nose (rhinitis)
tremor
unconscious behavior (automatism)
upper respiratory tract infection
vomiting
Rarely, the use of Apexidone Tablet may cause the following side-effects:
a state of near-unconsciousness
a sudden feeling of cold (rigors)
abnormal coordination
abnormal crying
abnormal gait
absence of menstrual period (amenorrhoea)
accumulation of fluid
acne
an adverse drug reaction of the skin (drug eruption)
an eye syndrome in which iris slips towards the area of an incision during cataract surgery (intraoperative floppy iris syndrome)
antiemetic effect
back pain
balance disorder
breast discomfort
breast pain
chapped lips (cheilitis)
chest discomfort
chest pain
chills
collection of hardened feces in the rectum (faecaloma)
dandruff
dangerously excessive intake of water (polydipsia)
decreased libido
decreased response of the skin to touch and pain (hypoesthesia)
decreased sexual drive (sexual dysfunction)
decreased taste sensitivity
decreased weight
difficult urination
difficulty in erection (erectile dysfunction)
difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
discharge from the breasts
disruption of body temperature regulation
disturbance in attention
disturbed focus
drug withdrawal syndrome in newborn babies
dry eye (xerophthalmia)
dry skin
ear pain
eczema
ejaculation disorder
excessive passing of gas
extraordinary daytime urinary frequency (pollakiuria)
eye movement disorder
eye rolling
eyelid margin crusting
fast, shallow breathing (hyperventilation)
feeling abnormal
feeling of discomfort
flushing
frequent passing of urine (micturition frequency)
fungal infection of the nails (onychomycosis)
glucose present in urine
hair loss
hives
inability to control bowel movements (faecal incontinence)
inability to pass urine
inability to reach orgasm (anorgasmia)
inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion
increase in a type of white blood cells
increased and decreased appetite
increased blood creatine phosphokinase enzyme
increased body temperature
increased heartbeat
increased tears
inflammation of the tonsils (tonsillitis)
infrequent menstrual periods (oligomenorrhoea)
involuntary laughing and crying
irregular or absent periods (anovulation)
joint stiffness
joint swelling
lack of emotion
lack of energy
lack of interest (apathy)
lack of muscle coordination
leg cramps
leg pain
low body weight (anorexia)
menstrual disorders
muscle or skeletal pain
muscle rigidity
muscle spasms
muscle weakness
nasal congestion
neck pain
nervousness
nightmare
no emotional expression
oversensitivity of the eyes to light
pain in joints (arthralgia)
pain in pharynx and larynx
painful erection (priapism)
palpitations
parkinsonian gait
parkinsonian rest tremor
photophobia
postural dizziness
procedural pain
prolonged and irregular heartbeat
psychomotor hyperactivity
puberty occurring at an unusually early age (precocious puberty)
red, itchy rash and white scales (seborrhea)
redness of the eye (ocular hyperaemia)
reduced sense of touch (hypoaesthesia)
ringing in the ears
severe itching
shaking of the head (head titubation)
skin discolouration
skin disorder
skin lesion
sleep walking
sleep-related eating disorder
speech disorder
stomach and intestinal infection
sugar in the urine
swelling of body tissues due to fluid accumulation
swelling of the face
swollen breast tissue in men
thickening of the skin (hyperkeratosis)
thirst
unconscious behavior (automatism)
unresponsive stimuli
urinary incontinence
vaginal discharge (leukorrhea)
vertigo
weight gain
The following severe side-effects may also occur when using Apexidone Tablet:
twitching or jerking movements of the body (tardive dyskinesia)
Symptoms: involuntary movement of the tongue, involuntary movement of the mouth involuntary movement of the face
If this happens, contact the doctor immediately. The withdrawal of the medicine may be needed.
blood clots in the veins
Symptoms: swelling on the affected area, pain on the affected area redness on the affected area
If this happens, seek medical help immediately.
painful erection (priapism)
Symptoms: painful or prolonged erection
If such side-effect occurs, contact your doctor immediately.
increased blood sugar level (diabetes mellitus) (production of excessive acids in the blood (diabetic ketoacidosis), coma or can be possibly fatal)
Symptoms: excessive thirst, increased urination, increased appetite weakness
If these symptoms appear, perform the test for fasting blood glucose level. The discontinuation of medicine may be needed.
decreased white blood cells
Symptoms: low white blood cell count, fever infection
Monitor the patients with a history of low white blood cell count during the therapy for such symptoms. Stop using Apexidone if a decrease in cell count is seen.
stroke (when used elderly patients with dementia related mental disorder (dementia-related psychosis)) (can be possibly fatal)
Symptoms: mental state changes, numbness of the face, numbness of the arms, numbness of the legs slurred speech
Do not use Apexidone in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis.
a rare life-threatening reaction to the medicines used to treat mental disorders (neuroleptic malignant syndrome) (can be possibly fatal)
Symptoms: muscle stiffness, fever, reduced level of consciousness, sweating, altered mental status, irregular pulse, irregular blood pressure, increased or irregular heartbeat, increased creatine phosphokinase level, muscle breakdown acute kidney failure
If this happens, stop using antipsychotic drugs immediately. The treatment should be given according to the symptoms and the patient should be monitored carefully.
severe allergic reaction
Symptoms: fever, swollen mouth, swollen face, swollen lips, swollen tongue, shortness of breath, itching, skin rash low blood pressure
If this happens, ask your doctor immediately.
respiratory disorders
Symptoms: stuffy nose (rhinitis) inflammation of the pharynx (pharyngitis)
progressive neurological disorder (Parkinson disorder)
Symptoms: slow movement, sensation of stiffness, tightness of the muscles, sensation of freezing movement, slow shuffling walk, tremor while at rest, increased saliva, drooling, loss of expression, muscular rigidity, slowness of movement (bradykinesia), loss of muscle movement (akinesia), an inability to flex the neck forward (nuchal rigidity), parkinsonian gait blink in response to the several taps on forehead
Your doctor has prescribed Apexidone Tablet because they judge that the benefit is greater than the risk posed by side-effects. Many people using this medicine do not have serious side-effects. This page does not list all possible side-effects of Apexidone Tablet.
If you experience side-effects or notice other side-effects not listed above, contact your doctor for medical advice. You may also report side-effects to your local food and drug administration authority. You can look up the drug authority contact information from the Drug Authority Finder at TabletWise.com.
Warnings
Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
Patients with aspiration pneumonia and patients who have started antipsychotic therapy are at an increased risk. Such patients may suffer from regurgitation of food, difficulty in swallowing, and a spasm type pain (esophageal dysmotility) and sucking food into the airway (aspiration). Patients at risk for lung infection due to the inhaled food, saliva, or stomach acid into the lungs (aspiration pneumonia) should use Apexidone and other antipsychotic medicines with caution.
Seizures
Patients with schizophrenia and seizures are at an increased risk when using this medicine. These patients may suffer from seizures. It is advised to use this medicine with caution in the patients with a history of seizures.
Problems with muscle function
Patients using Apexidone are at an increased risk. These patients may develop a problem with thinking, judgment, or movement of muscles. In these patients, precaution is advised while operating heavy machinery.
Low white blood cell count
Patients with a history of a drug-induced low level of white blood cells and existing low white blood cell count are at an increased risk when using this medicine. These patients may suffer from low white blood cell count (leukopenia, neutropenia, and deficiency of granulocytes in the blood). It is advised to monitor the patient for fever and other signs or symptoms of infection. If a severely low level of white blood cells occurs then discontinue the use of this medicine.
Postural low blood pressure
Patients with a decrease in blood pressure, while standing up from sitting or lying down using Apexidone, are at an increased risk. These patients may suffer from low blood pressure, dizziness, rapid heartbeat and fainting. In these patients, a low dose of Apexidone is recommended to reduce the risk of low blood pressure. Also, precaution is advised when using Apexidone in patients with heart diseases such as heart attack, heart failure, heart rhythm abnormalities, a disease of blood vessels in the brain (cerebrovascular disease), dehydration and decreased blood volume. The monitoring of vital signs should also be considered.
High prolactin level (hyperprolactinemia)
Patients using Apexidone and patients with existing high level of blood prolactin (hyperprolactinaemia) are at an increased risk. In these patients, prolactin levels may be increased in the blood. Due to this, a milky discharge from the breast (galactorrhea), an absence of menstruation (amenorrhea), enlarged breasts in men (gynecomastia), and difficulty in erection (impotence) can occur. Long-standing high level of prolactin in blood when associated with abnormally low levels of the sex hormones (hypogonadism) may results in decreased bone density in both male and female. When using this medicine, caution is advised especially in patients with existing high level of blood prolactin or patients with chances of prolactin-dependent tumors.
High blood glucose level (hyperglycemia)
Patients treated with atypical antipsychotics are at an increased risk. These patients may suffer from a high buildup of acids in the blood (ketoacidosis), coma, or fatality. If this happens, discontinue using this medicine. Some patients may need anti-diabetic treatment.
Repetitive involuntary body movements (tardive dyskinesia)
Patients who have started antipsychotic therapy are at an increased risk. These patients may develop irreversible or involuntary muscle movements. If this happens, discontinuation of Apexidone is advised.
Syndrome caused by antipsychotic drugs (neuroleptic malignant syndrome)
Patients using antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk. These patients may develop signs including muscle rigidity, fever, evidence of autonomic instability, altered mental status, the presence of myoglobin in the urine, increased level of enzyme creatinine phosphokinase and acute kidney failure. If this happens, stop using antipsychotic drugs immediately. The treatment should be given according to the symptoms and the patient should be monitored carefully.
Dementia-related psychosis
The older adults with dementia-related psychosis are at an increased risk when using this medicine. These patients may suffer from stroke, mini-stroke and mortality. In such patients, Apexidone should not be used.
Prolonged erection (priapism)
A prolonged erection (priapism) may occur with the use of this medicine. The severe priapism is corrected by surgical treatment.
Changes in body temperature
Patients treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk. These patients may experience an increase or decrease in body temperature. The patients who exposed to temperature extremes should use Apexidone and other antipsychotic medicines with caution.
Antiemetic effect
This medicine may cause an antiemetic effect. It may hide signs and symptoms of overdosage with several drugs or diseases such as brain and liver damage (Reye’s syndrome), intestinal obstruction, and brain tumor.
Possiblity of suicide
Patients with periods of abnormally elevated mood (bipolar mania) and severe mental disorder (schizophrenia) including adults and children are at an increased risk when using this medicine. There should be the chances of suicidal attempt in such patients. In such cases, the smallest effective dose is recommended to reduce the chances of overdose.
Brain disorders
Patients with brain disorders such as Parkinson’s disease or dementia with lewy bodies are at an increased risk when using this medicine. These patients may suffer from confusion, altered level of consciousness, postural instability with frequent falls, symptoms related to involuntary actions (extrapyramidal symptoms), and a syndrome caused by antipsychotic drugs (neuroleptic malignant syndrome). In these patients, this medicine should be used with caution.
Interactions with Apexidone
When two or more medicines are taken together, it can change how the medicines work and increase the risk of side-effects. In medical terms, this is called as a Drug Interaction.
Apexidone Tablet may interact with drugs acting on central nervous system and alcohol. The use of Apexidone with drugs acting on central nervous system and alcohol increases the risk of sleepiness or sedation. When Apexidone is used with other drugs that act on central nervous systems such as opiates, antihistamines and benzodiazepines and alcohol, caution should be used.
There may be an interaction of Apexidone with drugs with blood pressure lowering effects, which are used to treat high blood pressure. If Apexidone is used with blood pressure lowering drugs, it may enhance the blood pressure lowering effect of that drugs.
Apexidone Tablet interacts with levodopa and dopamine agonists, which are used to treat a Parkinson's disease. When Apexidone is used with levodopa and dopamine agonists, Apexidone blocks the effect of these drugs. If the use of Apexidone with levodopa and dopamine agonists is necessary, the lowest effective dose of each drug should be used to treat end-stage Parkinson's disease.
Special instructions need to be followed while taking this medicine along with cimetidine and ranitidine, which are used to treat stomach ulcers. If the Apexidone is used with cimetidine and ranitidine, the amount of Apexidone in the blood increases.
Your doctor's guidelines may need to be followed while taking this medicine along with clozapine, which is used to treat severe mental illness (schizophrenia). When Apexidone and clozapine are used together, the clearance of Apexidone is reduced.
Apexidone Tablet may interact with valproate, which is used to treat epileptic disease. If the Apexidone is used with valproate, the amount of valproate in the blood is mildly increased.
There may be an interaction of Apexidone with inhibitors of CYP2D6, CYP3A4, P-gp and other CYP isoenzymes. When Apexidone and CYP2D6 inhibitors (for example, paroxetine, quinidine and fluoxetine) are used together, the amount of Apexidone increases in the blood and lowers the level of its metabolite. When Apexidone and CYP3A4, P-gp inhibitors (for example, itraconazole) are used together, the amount of active fraction of Apexidone increases in the blood. When the use of Apexidone with CYP2D6 inhibitors, CYP3A4, P-gp inhibitors is initiated or stopped, dosage adjustment may be required.
Apexidone Tablet interacts with fluoxetine and paroxetine, which are used to treat depression. If the Apexidone is used with fluoxetine or paroxetine, the amount of Apexidone is increased in the blood. When the use of Apexidone with fluoxetine and paroxetine is initiated or stopped, the dosage of #NAME should be re-evaluated.
Special instructions need to be followed while taking this medicine along with carbamazepine and other enzyme inducers, which is used to control and prevent seizures. When Apexidone is used with carbamazepine and other enzyme inducers such as phenytoin and phenobarbital, the amount of metabolite of Apexidone decreases in the blood.
Your doctor's guidelines may need to be followed while taking this medicine along with drugs that prolong the heartbeat (QT interval). When Apexidone is used with drugs that prolong the heartbeat such as antiarrhythmics, tricyclic antidepressants, tetracyclic antidepressants, antihistamines, other antipsychotics, antimalarials and with medicines causing electrolyte imbalance, bradycardia, or those which prevent the breakdown of Apexidone by liver, caution should be taken.
Apexidone Tablet may interact with furosemide, which is used to treat fluid accumulation in heart, kidney or liver diseases. When Apexidone is used with furosemide, it can cause loss of water from the body which can be possibly fatal in the elderly patients with dementia. The use of Apexidone with furosemide should be avoided in the elderly patients with dementia.
There may be an interaction of Apexidone with paliperidone, which is used to treat mental or mood disorders. The use of Apexidone with paliperidone may lead to an increased amount of total active metabolite in the body. The use of Apexidone with paliperidone is not recommended.
Apexidone Tablet interacts with rifampicin, which is used to treat bacterial infection. When Apexidone is used with rifampicin, the amount of active metabolite of Apexidone in the blood decreases.
Special instructions need to be followed while taking this medicine along with ketoconazole, which is used to treat fungal infection. When Apexidone is used with ketoconazole, the amount of Apexidone in the blood increases and the amount of metabolite of Apexidone decreases.
Your doctor's guidelines may need to be followed while taking this medicine along with phenothiazines, which are used to treat mental disorders. When Apexidone is used with phenothiazines, may increase the amount of Apexidone in the blood.
This page does not contain all the possible interactions of Apexidone Tablet. Share a list of all medicines that you use with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dose of any medicines without the approval of your doctor.
Traveling With Medication
Ensure that you carry enough doses of each of your prescription medicines to last the entire trip. The best place to store your medicines is in the carry on baggage. However, while flying, if carrying liquid medicines, make sure you do not go over the limits imposed for carry-on liquids.
While traveling overseas, make sure that you can carry each of your prescription medicines legally to your destination country. One way to ensure this is by checking with your destination country's embassy or website.
Make sure that you carry each of your medicines in their original packaging, which should typically include your name and address, and the details of the prescribing doctor.
If your travel involves crossing time zones, and you are required to take your medicine as per a fixed schedule, make sure that you adjust for the change in time.
Expired Medication
Taking a single dose of expired Apexidone is unlikely to cause a side-effect. However, please discuss with your doctor or pharmacist, if you feel unwell or sick. An expired medicine may become ineffective in treating your prescribed conditions. To be on the safe side, it is important not to use an expired drug. You are much safer by always keeping a fresh supply of unexpired medicines.
Safe Disposal of Medication
If there are disposal instructions on the package, please follow the instructions.
If there are medicine take-back programs in your country, you should contact the respective authority to arrange for the disposal of the medicine. For example, in the USA, the Drug Enforcement Administration regularly hosts National Prescription Drug Take-Back events.
If there are no take-back programs, mix the medicine with dirt and place them in a sealed plastic bag. Throw the plastic bag in your household trash. Separately, remove all personal information including the prescription label from the medicine packaging and then dispose off the container.
If specifically indicated on the medicine package that it needs to be flushed down the toilet when no longer needed, perform the required step.
Write a review
Your Name:Your Review: Note: HTML is not translated!
Rating: Bad Good
Enter the code in the box below: