- Anti-hestaminic & Respiratory Drugs (20)
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs (197) +-
- Baby & Mom (1346) +-
- Baby & Mom > Bath, skin & Hair > Skin Care > wibes (52)
- Beauty (3129) +-
- Beauty > Skin Care > whitening (309)
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response (885) +-
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response > ANTI-FUNGAL (11)
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response > Chemotherapeutic Agents > Hormone Antagonists >Enzyme Inhibitors (290)
- CIRCULATORY DISTURBANCE AGENTS (24)
- Diet & Fitness Products (284) +-
- DRUG AFFECTING CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (191)
- HEMATOLOGY (39)
-
Medical Supplies (506)
+-
- Chemicals & Disinfectants (19)
- Dental Supplies (31)
- Devices & Instruments (11)
- Diabetic Supplies (121)
- General Medical Supplies (21)
- I.V & Medical Solution (0)
- Intensive Care Unit & Anesthesia Supplies (0)
- KIDNEY UNIT SUPPLIES (21)
- Lab Supplies (3)
- Miscellaneous (21)
- Neonatal Unit Supplies (0)
- Operation Room Supplies (2)
- Sanitary (5)
- Sterilization Supplies (1)
- Surgical Sutures (4)
- Syringes (3)
-
Medicines & Health (2727)
+-
- Allergy & Sinus (97)
- Children's Health Care (54)
- Cough, Cold & Flu (283)
- Digestive Health & Nausea (231)
- Ear, Nose & Throat Care (181)
- Eye Care (124)
- Feminine Care (323)
- Foot Care (12)
- Orthopaedic Appliances (1)
- Pain Relief & Management (244)
- Pill Organizer (2)
- Skin Treatments (863)
- Sleep & Snoring Aids (2)
- Support & Braces (8)
- Medicines & health > Gout releif (42)
- Natural & Organic Products (81) +-
- OTC > Analgesics > Anti-inflammatory Drugs (44)
-
Personal Care (3363)
+-
- Bath & Body (273)
- Deodorant & Anti-perspirants (191)
- Ear, Nose & Throat Care (177)
- Eye Care (131)
- Feminine Care (372)
- Foot Care (20)
- Hair Care (511)
- Home Tests & Monitorings (14)
- Incontinence (7)
- Lip Care (26)
- Massage & Relaxation (17)
- Natural & Organic Personal Care (7)
- Oral Care (91)
- Pregnancy & Fertility (64)
- Shaving & Grooming (75)
- Sun Care (80)
-
Prescription Drugs (2935)
+-
- Analgesics (184)
- Cardiovascular System (377)
- Drugs Affecting Musculoskeletal System (65)
- Drugs Used In Infections (56)
- Ear & Nose Drugs (2)
- Endocrine System (177)
- Gastrointestinal Tract (243)
- Gastrointestinal Tract > Hepatology > Liver treatment (60)
- GYNECOLOGY (2)
- Miscellaneous (11)
- NEPHROLOGY > URINARY SYSTEM > RENAL DISORDERS > URINARY TRACT DISORDERS (47)
- NEUROLOGY (228)
- Nutrients & Blood Electrolytes (2)
- Respiratory System (154)
- SKIN > NAILS > HAIR > TOPICAL PREPARATIONS (115)
- Vaccines (1)
- Prescription drugs > Cardiovascular system > Anti-hypertension drugs (242)
- Sexual Wellness (304) +-
- Vitamins & Minerals Supplements (1232) +-
Ex Tax: 900EGP
Example
You can return the product within 14 days of purchase.
ReturnsYou can return the product within 14 days of purchase.

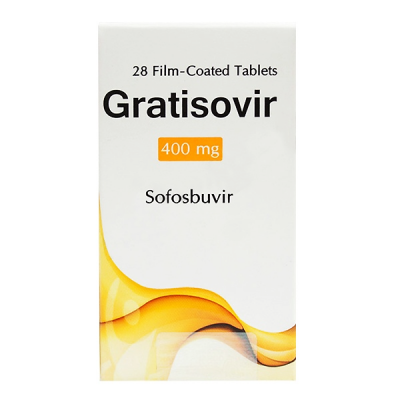
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablet
400mg (Sovaldi, generic)
Chronic Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Infection
Indicated as a component of a combination antiviral regimen for HCV mono-infection and HCV/HIV-1 coinfection
Treatment regimen and duration are dependent on both viral genotype and patient population
Genotype 1 or 4: 400 mg PO qDay plus ribavirin and peginterferon alfa for 12 weeks; may consider sofosbuvir plus ribavirin for 24 weeks in genotype 1 patients ineligible to receive peg-interferon-based regimen
Genotype 2: 400 mg PO qDay plus ribavirin for 12 weeks
Genotype 3: 400 mg PO qDay plus ribavirin for 24 weeks
Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma awaiting liver transplantation:
- For prevention of post-transplant HCV reinfection
- 400 mg PO qDay plus ribavirin for up to 48 weeks or until the time of liver transplantation, whichever occurs first
Ribavirin dosage regimen with sofosbuvir (genotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4)
Take with food
- <75 kg : 500 mg PO BID
- ≥75 kg: 600 mg PO BID
- Renal impairment (CrCl ≤50 mL/min): Reduce dose (see prescribing information)
Peginterferon alfa regimen with sofosbuvir (genotype 1 or 4)
- Peginterferon alfa 2a: 180 mcg SC weekly
- Peginterferon alfa 2b: 1.5 mcg/kg/week SC; not to exceed 150 mcg/week
- Renal impairment (CrCl ≤50 mL/min): Reduce dose (see prescribing information)
*Dosage Modification:
Reduction of sofosbuvir dose not recommended
Discontinue sofosbuvir therapy if the agents used in combination are discontinued
Genotypes 1 and 4
Serious adverse reactions potentially related to peginterferon alfa and/or ribavirin: Should reduce or discontinue dose of peginterferon alfa and/or ribavirin following the recommendations of their respective prescribing information
Genotypes 2 and 3
- Serious adverse reaction potentially related to ribavirin: Modify or discontinue ribavirin dose
- Hemoglobin <10 g/dL without cardiac disease: Reduce ribavirin dose to 600 mg/day PO divided BID with food
- Hemoglobin <8.5 g/dL without cardiac disease: Discontinue ribavirin
- Cardiac disease and hemoglobin decreased ≥2 g/dL during 4 week period: Reduce ribavirin dose to 600 mg/day PO divided BID with food
- Cardiac disease and hemoglobin <12 g/dL despite 4 weeks at reduced dose: Discontinue ribavirin
- After discontinuing the dose may attempt to restart ribavirin at 600 mg PO divided bid and further increase it to 800 mg PO divided bid; increasing the dose to 1000-1200 mg/day not recommended
Renal impairment
- Mild or moderate: No adjustments required
- Severe (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m²) or ESRD: No dosage recommendation can be given owing to higher exposures (up to 20-fold) of the predominant sofosbuvir metabolite
Hepatic impairment
Mild, moderate, or severe (Child-Pugh Classes A, B or C): No dose adjustments required
Decompensated cirrhosis: Not established
*Dosing Considerations:
Efficacy has been established in combination with peginterferon alfa and ribavirin in HCV genotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4 infected subjects including hepatocellular carcinoma meeting Milan criteria (awaiting liver transplantation) and those with HCV/HIV-1 coinfection
Must not be used as monotherapy; if peginterferon alfa or ribavirin is discontinued for any reason, sofosbuvir must also be discontinued
Test all patients for evidence of current or prior hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection before initiating treatment with HCV direct acting antivirals (DDAs)
Drug drug Interactions
- Contraindicated (0)
- Serious - Use Alternative (17)
amiodarone
carbamazepine
eliglustat
erdafitinib
fosphenytoin
lasmiditan
leniolisib
oxcarbazepine
phenobarbital
phenytoin
rifabutin
rifampin
rifapentine
sotorasib
St John's Wort
tepotinib
tipranavir
- Monitor Closely (23)
acalabrutinib
apalutamide
berotralstat
danicopan
darolutamide
elagolix
elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF
encorafenib
fostemsavir
istradefylline
lonafarnib
mavorixafor
momelotinib
oteseconazole
regorafenib
safinamide
sarecycline
stiripentol
tafamidis
tafamidis meglumine
tenofovir DF
tucatinib
vadadustat
- Minor (0)
Adverse Effects
>10%:Sofosbuvir plus ribavarin (12 weeks)
Fatigue (38%)
Headache (24%)
Nausea (22%)
Insomnia (15%)
Pruritus (11%)
Sofosbuvir plus ribavarin (24 weeks)
Fatigue (30%)
Headache (30%)
Nausea (13%)
Insomnia (16%)
Pruritus (27%)
Asthenia (21%)
Diarrhea (12%)
Sofosbuvir plus ribavarin plus peg-interferon (12 weeks)
Fatigue (59%)
Headache (36%)
Nausea (34%)
Insomnia (25%)
Pruritus (17%)
Anemia (21%)
Rash (18%)
Decreased appetite (18%)
Chills (17%)
Influenza-like illness (16%)
Pyrexia (18%)
Diarrhea (12%)
Neutropenia (17%)
Myalgia (14%)
Irritability (13%)
Sofosbuvir plus ribavarin plus peg-interferon (24 weeks)
Fatigue (55%)
Headache (44%)
Nausea (29%)
Insomnia (29%)
Pruritus (17%)
Anemia (12%)
Rash (18%)
Decreased appetite (18%)
Chills (18%)
Influenza-like illness (18%)
Pyrexia (14%)
Diarrhea (17%)
Neutropenia (12%)
Myalgia (16%)
Irritability (16%)
1-10%:
Sofosbuvir plus ribavarin (12 weeks)
Anemia (10%)
Asthenia (6%)
Rash (8%)
Decreased appetite (6%)
Chills (2%)
Influenza-like sickness (3%)
Pyrexia (4%)
Diarrhea (9%)
Myalgia (6%)
Irritability (10%)
Sofosbuvir plus ribavarin (24 weeks)
Anemia (6%)
Rash (9%)
Decreased appetite (6%)
Chills (2%)
Influenza-like sickness (6%)
Pyrexia (4%)
Myalgia (9%)
Irritability (10%)
<1%:
Neutropenia
Pancytopenia
Severe depression (particularly in patients with pre-existing psychiatric illness)
Postmarketing Reports:
Bradycardia
Warnings
|
Black Box Warnings HBV reactivation has been reported in HCV/HBV coinfected patients who were undergoing or had completed treatment with DDAs and were not receiving HBV antiviral therapy Some cases have resulted in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death Monitor HCV/HBV coinfected patients for hepatitis flare or HBV reactivation during HCV treatment and post-treatment follow-up Initiate appropriate patient management for HBV infection as clinically indicated |
Contraindications
Contraindications applicable to combination therapy
Combination with ribavirin
- Hypersensitivity
- Pregnancy or planning pregnancy, including men whose female partners are pregnant/planning to get pregnant
- CrCl <50 mL/min
- Pancreatitis
- Hemoglobinopathies (eg, thalassemia major, sickle cell anemia)
- Coadministration with didanosine
- Autoimmune hepatitis, decompensated liver disease (Child-Pugh class B, C)
- Use in neonates, infants (contains benzyl alcohol)
Combination with peg-interferon alfa
- Autoimmune hepatitis, decompensated liver disease (Child-Pugh class B, C)
- Use in neonates, infants (contains benzyl alcohol)
Cautions
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation has been reported in HCV/HBV coinfected patients who were undergoing or had completed treatment with HCV DDAs, and who were not receiving HBV antiviral therapy; HBV reactivation is characterized as an abrupt increase in HBV replication manifesting as a rapid increase in serum HBV DNA level (see Black Box Warnings and Dosing Considerations)
Drugs that are potent P-gp inducers in the intestine (eg, rifampin, St. John’s wort) may significantly decrease sofosbuvir plasma concentrations
Serious symptomatic bradycardia may occur in coadministration with amiodarone in combination with another direct acting antiviral (DAA), particularly in patients also receiving beta blockers, or those with underlying cardiac comorbidities and/or advanced liver disease; coadministration is not recommended, if no alternative exists, inpatient cardiac monitoring is recommended for the first 48 hr and then daily home monitoring for at least the first 2 weeks
Must NOT be used as monotherapy
Use with other drugs containing sofosbuvir not recommended
Combination with ribavirin
- Ribavirin may cause birth defects and fetal death; avoid pregnancy in female patients and female partners of male patients; patients must have a negative pregnancy test prior to therapy; use 2 or more forms of contraception, 1 of these forms of contraception can be a combined oral contraceptive product containing at least 1 mg of norethindrone (lower doses of norethindrone and other forms of hormonal contraception have not been studied or are contraindicated)
- Risk of hemolytic anemia
- Anemia associated with treatment may result in worsening of cardiac disease
- Potential carcinogen effects
- Ocular disorders reported when ribavirin is used in combination therapy with alpha interferons (eg, decrease or loss of vision, retinopathy including macular edema, retinal artery or vein, thrombosis, retinal hemorrhages; cotton wool spots, optic neuritis, papilledema, serous retinal detachment)
- Study in boys showed growth rate inhibited (ie, height percentile decreases) with peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin
- Pancytopenia and bone marrow suppression reported when coadministered with pegylated interferon and azathioprine
Combination with peg-interferon alfa
- Discontinue STAT if progressive ALT increases despite dose reduction or accompanied with increased bilirubin or signs of hepatic decompensation
- Caution in renal impairment
- Risk of suicidal ideation and psychoses; discontinued if severe depression occurs
- Safety and efficacy not been established in patients with liver and other transplantations; as with other alpha interferons, liver and renal graft rejections have been reported
- May cause myelosuppression; discontinue therapy (at least temporarily) if platelet count <25,000/mm³ or ANC <500/mm³
- Will likely experience flu-like symptoms in early part of treatment
- May cause development of exacerbation of several pathologic conditions
- Reduce/discontinue if moderate/severe depression, see Manufacturer's package insert
- In hepatic impairment, reduce/discontinue as suggested by Manufacturer's package insert
Drug interaction overview
- Frequent monitoring of relevant laboratory parameters (eg, International Normalized Ratio [INR] in patients taking warfarin, blood glucose levels in diabetic patients) or drug concentrations of concomitant medications such as cytochrome P450 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index (eg, certain immunosuppressants) is recommended to ensure safe and effective use; dose adjustments of concomitant medications may be necessary
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
If therapy administered with ribavirin or peginterferon alfa and ribavirin, the combination regimen is contraindicated in pregnant women and in men whose female partners are pregnant; refer to ribavirin and/or peginterferon alfa prescribing information for more information on ribavirin-and peginterferon alfa-associated risks of use during pregnancy
No adequate human data available to establish whether or not drug poses a risk to pregnancy outcomes
Animal data
In animal reproduction studies, no evidence of adverse developmental outcomes observed with sofosbuvir at exposures greater than those in humans at recommended human dose (RHD); during organogenesis in the rat and rabbit, systemic exposures (AUC) to predominant circulating metabolite of sofosbuvir (GS-331007) were ≥5 (rats) and 12 (rabbits) times the exposure in humans at the RHD; in the rat pre/postnatal development study, maternal systemic exposure (AUC) to GS-331007 was ≥6 times exposure in humans at RHD
Lactation
Not known whether sofosbuvir or metabolites are present in human breast milk, affect human milk production or have effects on breastfed infant; the predominant circulating metabolite of sofosbuvir (GS-331007) was the primary component observed in the milk of lactating rats, without effect on nursing pups
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for therapy and any potential adverse effects on breastfed child from drug or from underlying maternal condition
If drug is administered with ribavirin, the nursing mother’s information for ribavirin also applies to this combination regimen; refer to ribavirin prescribing information for more information on use during lactation
*Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk.
C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done.
D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk.
X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist.
NA: Information not available.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Nucleotide prodrug that undergoes metabolism to the active uridine analog triphosphate, an inhibitor of HCV NS5B RNA-dependent polymerase; its inhibition in turn suppresses viral replication
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Peak plasma time: 0.5-2 hr (sofosbuvir); 2-4 hr (metabolite GS-331007)
AUC when coadministered with ribavirin (with or without peg-interferon): 828 ng•hr/mL (sofosbuvir); 6790 ng•hr/mL (metabolite GS-331007)
Distribution
Plasma bound: 61-65% (sofosbuvir); minimal for metabolite GS-331007
Metabolism
Liver
Substrate: P-gp transporter and breast cancer resistance protein (substrate for sofosbuvir but not metabolite GS-331007)
Elimination
Excretion: Urine (78% metabolite GS-331007; 3.5% sofosbuvir)
Half-life: 0.4hr (sofosbuvir); 27 hr (metabolite GS-331007)
Pharmacogenomics
Available data on genotype 5 or 6 HCV infection insufficient for dosing recommendations
Genotype 2 or 3: Sustained virologic response (SVR): The response to the addition of peg-interferon alfa to the sofosbuvir/ribavirin combination therapy was not significantly different, in clinical trials, compared to the sofosbuvir/ribavirin combination alone.
Write a review
Your Name:Your Review: Note: HTML is not translated!
Rating: Bad Good
Enter the code in the box below: