- Anti-hestaminic & Respiratory Drugs (17)
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs (170) +-
- Baby & Mom (1213) +-
- Baby & Mom > Bath, skin & Hair > Skin Care > wibes (50)
- Beauty (2548) +-
- Beauty > Skin Care > whitening (259)
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response (476) +-
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response > ANTI-FUNGAL (4)
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response > Chemotherapeutic Agents > Hormone Antagonists >Enzyme Inhibitors (155)
- CIRCULATORY DISTURBANCE AGENTS (19)
- Diet & Fitness Products (218) +-
- DRUG AFFECTING CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (163)
- Drugs affecting CNS >Anti- epileptic (65)
-
Medical Supplies (470)
+-
- Chemicals & Disinfectants (17)
- Dental Supplies (27)
- Devices & Instruments (8)
- Diabetic Supplies (110)
- General Medical Supplies (21)
- I.V & Medical Solution (0)
- Intensive Care Unit & Anesthesia Supplies (0)
- Kindney Unit Supplies (12)
- Lab Supplies (1)
- Miscellaneous (22)
- Neonatal Unit Supplies (0)
- Operation Room Supplies (3)
- Sanitary (5)
- Sterilization Supplies (0)
- Surgical Sutures (3)
- Syringes (2)
-
Medicines & Health (2396)
+-
- Allergy & Sinus (91)
- Children's Health Care (52)
- Cough, Cold & Flu (282)
- Digestive Health & Nausea (202)
- Ear, Nose & Throat Care (159)
- Eye Care (114)
- Feminine Care (295)
- Foot Care (3)
- Orthopaedic Appliances (0)
- Pain Relief & Management (205)
- Pill Organizer (2)
- Skin Treatments (700)
- Sleep & Snoring Aids (0)
- Support & Braces (6)
- Medicines & health > Gout releif (41)
- Natural & Organic Products (78) +-
- OTC > Analgesics > Anti-inflammatory Drugs (43)
-
Personal Care (2835)
+-
- Bath & Body (214)
- Deodorant & Anti-perspirants (175)
- Ear, Nose & Throat Care (152)
- Eye Care (120)
- Feminine Care (332)
- Foot Care (11)
- Hair Care (374)
- Home Tests & Monitorings (16)
- Incontinence (7)
- Lip Care (19)
- Massage & Relaxation (18)
- Natural & Organic Personal Care (7)
- Oral Care (75)
- Pregnancy & Fertility (55)
- Shaving & Grooming (53)
- Sun Care (52)
- Prescribtion drugs > cardiovascular system > Hypertention drugs (323) +-
-
Prescription Drugs (2817)
+-
- Analgesics (172)
- Cardiovascular System (327)
- Drugs Affecting Musculoskeletal System (59)
- Drugs Used In Infections (49)
- Ear & Nose Drugs (2)
- Endocrine System (154)
- Gastrointestinal Tract (214)
- Gastrointestinal Tract (196)
- GYNECOLOGY (2)
- Miscellaneous (6)
- NEPHROLOGY > URINARY SYSTEM > RENAL DISORDERS > URINARY TRACT DISORDERS (22)
- NEUROLOGY (190)
- Nutrients & Blood Electrolytes (2)
- prescription drugs > cardiovascular system >Anti-hypertensive drugs (72)
- Prescription Drugs > Gastrointestinal Tract > Hepatology > Liver treatment (55)
- Respiratory System (115)
- SKIN > NAILS > HAIR > TOPICAL PREPARATIONS (29)
- Vaccines (1)
- Sexual Wellness (196) +-
- strong anti-emetic & adjuvent used with anti-neoplastic (0)
- Vitamins & Minerals Supplements (1060) +-
Ex Tax: 12EGP
Example
You can return the product within 14 days of purchase.
ReturnsYou can return the product within 14 days of purchase.

Composition
Each dosage unit contains
Enteric-coated Tablet
SR Film-coated Tablet
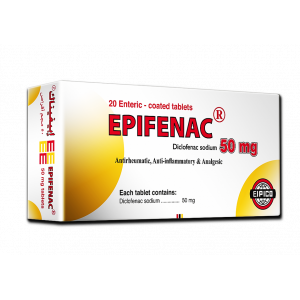
Diclofenac sodium
25 mg or 50 mg
75 mg or 100 mg
Inactive Ingredients:
EPIFENAC 25 mg Enteric-coated Tablets:
Lactose monohydrate, maize starch, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone XL, magnesium stearate, colloidal silicon dioxide, sodium starch glycolate, Cellulpse acetate phathalate, quinoline yellow, castor oil, methanol, acetone.
EPIFENAC 50 mg Enteric-coatedTablets:
Lactose monohydrate, maize starch, microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, sodium starch glycolate, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, cellulose acetate phthalate, castor oil, iron oxide red, iron oxide black.
EPIFENAC 75 mg Sustained Release Film-coated Tablets:
Lactose, avicel PH 101, polyvinyl pyrollidone K 30, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose K15M, magnesium stearate, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose 2910, iron oxide red, Polyethylene glycol 4000, titanium dioxide.
EPIFENAC 100 mg Sustained Release Film-coated Tablets:
Lactose monohydrate, avicel PH 101, polyvinyl pyrollidone K 30, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose K15M, magnesium stearate, hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose 2910, FD&C red No 40 lake, Polyethylene glycol 4000, titanium dioxide.
Therapeutic Indications
Adults and Elderly:
Relief of all grades of pain and inflammation in a wide range of conditions, including:
Arthritic conditions: Osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, acute gout.
Acute musculo-skeletal disorders: Periarthritis (for example frozen shoulder), tendinitis, tenosynovitis, bursitis.
Other painful conditions resulting from trauma including: fracture, low back pain, sprains, strains, dislocations, orthopaedic, dental and other minor surgery.
EPIFENAC 25 mg Tablets:
Children (aged 1-12 years):
Juvenile chronic arthritis.
EPIFENAC 50 mg Tablets are not recommended for children.
EPIFENAC 75 mg and 100 mg SR Tablets are not suitable for children.
Dosage and Administration
Undesirable effects may be minimised by using the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary to control symptoms.
For oral administration.
EPIFENAC 25 mg, 50 mg Tablets: 75-150 mg daily in two or three divided doses.
EPIFENAC 75 mg SR Tablets: One tablet once or twice daily, taken whole with liquid, preferably at meal times.
EPIFENAC 100 mg SR Tablets: One tablet daily, taken whole with liquid, preferably at meal times.
The recommended maximum daily dose of EPIFENAC is 150 mg.
Special populations:
Elderly:
Although the pharmacokinetics of EPIFENAC are not impaired to any clinically relevant extent in elderly patients, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be used with particular caution in such patients who generally are more prone to adverse reactions. In particular it is recommended that the lowest effective dosage be used in frail elderly patients or those with a low body weight and the patient should be monitored for GI bleeding during NSAID therapy.
Renal impairment:
Diclofenac is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment. No specific studies have been carried out in patients with renal impairment, therefore, no specific dose adjustment recommendations can be made. Caution is advised when administering EPIFENAC to patients with mild to moderate renal impairment.
Hepatic impairment:
Diclofenac is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment. No specific studies have been carried out in patients with hepatic impairment, therefore, no specific dose adjustment recommendations can be made. Caution is advised when administering EPIFENAC to patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment.
Pediatric population:
EPIFENAC 25 mg Tablets:
Children (aged 1-12 years): 1-3 mg/kg per day in divided doses.
EPIFENAC 50 mg Tablets are not recommended for children.
EPIFENAC 75 mg and 100 mg SR Tablets are not suitable for children.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or any of the excipients.
Active, gastric or intestinal ulcer, bleeding or perforation.
History of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation, relating to previous NSAID therapy.
Active, or history of recurrent peptic ulcer/haemorrhage (two or more distinct episodes of proven ulceration or bleeding.
Last trimester of pregnancy.
Severe hepatic, renal or cardiac failure.
Like other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), EPIFENAC is also contraindicated in patients in whom attacks of asthma, angioedema, urticaria or acute rhinitis are precipitated by ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Established congestive heart failure (NYHA II-IV), ischemic heart disease, peripheral arterial disease and/or cerebrovascular disease.
NSAIDs are contraindicated for the treatment of peri-operative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery.
In patients with sugar intolerance.
Warnings and Precautions
General:
Undesirable effects may be minimised by using the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary to control symptoms.
The concomitant use of EPIFENAC with systemic NSAIDs including cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors should be avoided due to the absence of any evidence demonstrating synergistic benefits and the potential for additive undesirable effects.
Caution is indicated in the elderly on basic medical grounds. In particular, it is recommended that the lowest effective dose be used in frail elderly patients or those with a low body weight.
As with other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including diclofenac , allergic reactions, including anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions, can also occur without earlier exposure to the drug.
Like other NSAIDs, diclofenac may mask the signs and symptoms of the infection due to its pharmacodynamic properties.
EPIFENAC contains lactose and therefore is not recommended for patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, severe lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Gastrointestinal effects:
Gastrointestinal bleeding (haematemesis, melaena) ulceration or perforation which can be fatal has been reported with all NSAIDs including diclofenac and may occur at any time during treatment, with or without warning symptoms or a previous history of serious GI events. They generally have more serious consequences in the elderly. If gastrointestinal bleeding or ulceration occurs in patients receiving diclofenac, EPIFENAC should be withdrawn.
As with all NSAIDs, including diclofenac close medical surveillance is imperative and particular caution should be excised when prescribing EPIFENAC in patients with symptoms indicative of gastrointestinal disorders, or with a history suggestive of gastric or intestinal ulceration, bleeding or perforation. The risk of GI bleeding, ulceration or perforation is higher with increasing NSAID doses including diclofenac, and in patients with a history of ulcer, particularly if complicated with haemorrhage or perforation.
The elderly have increased frequency of adverse reactions to NSAIDs especially gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation which may be fatal.
To reduce the risk of GI toxicity in patients with a history of ulcer, particularly if complicated with haemorrhage or perforation, and in the elderly, the treatment should be initiated and maintained at the lowest effective dose.
Combination therapy with protective agents (e.g. misoprostol or proton pump inhibitors) should be considered for these patients, and also for patients requiring concomitant use of medicinal products containing low dose acetylsalicylic acid (ASA/aspirin) or medicinal products likely to increase gastrointestinal risk.
Patients with a history of GI toxicity, particularly when elderly, should report any unusual abdominal symptoms (especially GI bleeding).
Caution is recommended in patients receiving concomitant medications which could increase the risk of ulceration or bleeding, such as systemic corticosteroids, anticoagulants such as warfarin, Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) or anti-platelet agents such as acetylsalicylic acid.
Close medical surveillance and caution should be exercised in patients with ulcerative colitis, or with Crohn's disease as these conditions may be exacerbated.
Hepatic effects:
Close medical surveillance is required when prescribing EPIFENAC to patients with impairment of hepatic function as their condition may be exacerbated.
As with other NSAIDs, including diclofenac, values of one or more liver enzymes may increase. During prolonged treatment with EPIFENAC, regular monitoring of hepatic function is indicated as a precautionary measure.
If abnormal liver function tests persist or worsen, clinical signs or symptoms consistent with liver disease develop or if other manifestations occur (eosinophilia, rash), EPIFENAC should be discontinued.
Hepatitis may occur with diclofenac without prodromal symptoms.
Caution is called for when using EPIFENAC in patients with hepatic porphyria, since it may trigger an attack.
Renal effects:
As fluid retention and oedema have been reported in association with NSAIDs therapy, including diclofenac, particular caution is called for in patients with impaired cardiac or renal function, history of hypertension, the elderly, patients receiving concomitant treatment with diuretics or medicinal products that can significantly impact renal function, and those patients with substantial extracellular volume depletion from any cause, e.g. before or after major surgery. Monitoring of renal function is recommended as a precautionary measure when using EPIFENAC in such cases. Discontinuation therapy is usually followed by recovery to the pre-treatment state.
Drug Interactions
The following interactions include those observed with diclofenac tablets and/or other pharmaceutical forms of diclofenac.
Lithium: If used concomitantly, EPIFENAC may increase plasma concentrations of lithium. Monitoring of the serum lithium level is recommended.
Digoxin: If used concomitantly, EPIFENAC may raise plasma concentrations of digoxin. Monitoring of the serum digoxin level is recommended.
Diuretics and Antihypertensive agents: Like other NSAIDs, concomitant use of EPIFENAC with diuretics and antihypertensive agents (e.g. beta-blockers, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors) may cause a decrease in their antihypertensive effect via inhibition of vasodilatory prostaglandin synthesis.
Therefore, the combination should be administered with caution and patients, especially the elderly, should have their blood pressure periodically monitored. Patients should be adequately hydrated and consideration should be given to monitoring of renal function after initiation of concomitant therapy periodically thereafter, particularly for diuretics and ACE inhibitors due to the increased risk of nephrotoxicity.
Drugs known to cause hyperkalemia: Concomitant treatment with potassium-sparing diuretics, ciclosporin, tracrolimus or trimethoprim may be associated with increased serum potassium levels, which should therefore be monitored frequently.
Anticoagulants and Anti-platelet agents: Caution is recommended since concomitant administration could increase the risk of bleeding.
Although clinical investigations do not appear to indicate that diclofenac has an influence on the effect of anticoagulants, there are isolated reports of an increased risk of haemorrhage in patients receiving diclofenac and anticoagulants concomitantly. Therefore, to be certain that no change in anticoagulant dosage is required, close monitoring of such patients is required. As with other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, diclofenac in a high dose can reversibly inhibit platelet aggregation.
Other NSAIDs including cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors and corticosteroids: Coadministration of diclofenac with other systemic NSAIDs or corticosteroids may increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding or ulceration. Avoid concomitant use of two or more NSAIDs.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): Concomitant administration of SSRI’s may increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Antidiabetics: Clinical studies have shown that diclofenac can be given together with oral antidiabetic agents without influencing their clinical effect. However there have been isolated reports of hypoglycaemic and hyperglycaemic effects necessitating changes in the dosage of the antidiabetic agents during treatment with diclofenac. For this reason, monitoring of the blood glucose level is recommended as a precautionary measure during concomitant therapy.
Methotrexate: Diclofenac can inhibit the tubular renal clearance of methotrexate hereby increasing methotrexate levels. Caution is recommended when NSAIDs, including EPIFENAC, are administered less than 24 hours before treatment with methotrexate, since blood concentrations of methotrexate may rise and the toxicity of this substance be increase. Cases of serious toxicity have been reported when methotrexate and NSAIDs including diclofenac are given within 24 hours of each other. This interaction is mediated through accumulation of methotrexate resulting from impairment of renal excretion in the presence of the NSAID.
Ciclosporin: Diclofenac, like other NSAIDs, may increase the nephrotoxicity of ciclosporin due to the effect on renal prostaglandins. Therefore, EPIFENAC should be given at doses lower than those that would be used in patients not receiving ciclosporin.
Tacrolimus: Possible increased risk of nephrotoxicity when NSAIDs are given with tacrolimus. This might be mediated through renal antiprostagladin effects of both NSAID and calcineurin inhibitor.
Quinolone antibacterials: Convulsions may occur due to an interaction between quinolones and NSAIDs. This may occur in patients with or without a previous history of epilepsy or convulsions. Therefore, caution should be exercised when considering the use of a quinolone in patients who are already receiving an NSAID.
Phenytoin: When using phenytoin concomitantly with EPIFENAC, monitoring of phenytoin plasma concentrations is recommended due to an expected increase in exposure to phenytoin.
Colestipol and Cholestyramine: These agents can induce a delay or decrease in absorption of diclofenac. Therefore, it is recommended to administer EPIFENAC at least one hour before or 4 to 6 hours after administration of colestipol/ cholestyramine.
Cardiac glycosides: Concomitant use of cardiac glycosides and NSAIDs in patients may exacerbate cardiac failure, reduce GFR and increase plasma glycoside levels.
Mifepristone: NSAIDs should not be used for 8-12 days after mifepristone administration as NSAIDs can reduce the effect of mifepristone.
Potent CYP2C9 inhibitors: Caution is recommended when co-prescribing EPIFENAC with potent CYP2C9 inhibitors (such as voriconazole), which could result in a significant increase in peak plasma concentrations and exposure to diclofenac due to inhibition of diclofenac metabolism.
Pregnancy and Lactation
Pregnancy:
Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis may adversely affect the pregnancy and/or the embryo/foetal development. Data from epidemiological studies suggest an increased risk of miscarriage and or cardiac malformation and gastroschisis after use of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor in early pregnancy. The absolute risk for cardiovascular malformation was increased from less than 1% up to approximately 1.5%.
The risk is believed to increase with dose and duration of therapy. In animals, administration of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor has shown to result in increased pre-and post-implantation loss and embryo-foetal lethality.
In addition, increased incidences of various malformations, including cardiovascular, have been reported in animals given a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor during organogenetic period. If EPIFENAC is used by a woman attempting to conceive, or during the 1st trimester of pregnancy, the dose should be kept as low and duration of treatment as short as possible.
During the third trimester of pregnancy, all prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors may expose the fetus to:
- cardiopulmonary toxicity (with premature closure of the ductus arteriosus and pulmonary hypertension).
- renal dysfunction, which may progress to renal failure with oligo-hydroamniosis.
The mother and the neonate, at the end of the pregnancy, to:
- possible prolongation of bleeding time, an anti-aggregating effect which may occur even at very low doses.
- inhibition of uterine contractions resulting in delayed or prolonged labour.
Consequently, EPIFENAC is contraindicated during the third trimester of pregnancy.
Lactation:
Like other NSAIDs, diclofenac passes into breast milk in small amounts. Therefore, EPIFENAC should not be administered during breast feeding in order to avoid undesirable effects in the infant.
Female fertility:
As with other NSAIDs, the use of EPIFENAC may impair female fertility and is not recommended in women attempting to conceive. In women who may have difficulties conceiving or who are undergoing investigation of infertility, withdrawal of EPIFENAC should be considered.
Effects on ability to drive and to use machines
Patients who experience visual disturbances, dizziness, vertigo, somnolence, central nervous system disturbances, drowsiness or fatigue while taking NSAIDs should refrain from driving or operating machinery.
Undesirable Effects
Adverse reactions are ranked under the heading of frequency, the most frequent first, using the following convention: Very common: (>1/10); Common (≥ 1/100, <1/10); Uncommon (≥ 1/1,000, <1/100); Rare (≥ 1/10,000, <1/1000); Very rare (<1/10,000); Not known: cannot be estimated from available data.
The following undesirable effects include those reported with other short-term or long-term use.
Blood and Lymphatic system disorders:
Very rare: Thrombocytopenia, leucopoenia, anaemia (including haemolytic and aplastic anaemia), agranulocytosis.
Immune system disorders:
Rare: Hypersensitivity, anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions (including hypotension and shock).
Very rare: Angioneurotic oedema (including face oedema).
Psychiatric disorders:
Very rare: Disorientation, depression, insomnia, nightmare, irritability, psychotic disorder.
Nervous system disorders:
Common: Headache, dizziness.
Rare: Somnolence, tiredness.
Very rare: Paraesthesia, memory impairment, convulsion, anxiety, tremor, aseptic meningitis, taste disturbances, cerebrovascular accident.
Unknown: Confusion, hallucinations, disturbances of sensation, malaise.
Eye disorders:
Very rare: Visual disturbance, blurred vision, diplopia.
Unknown: Optic neuritis.
Ear and Labyrinth disorders:
Common: Vertigo.
Very rare: Tinnitus, impaired hearing.
Cardiac disorders:
Very rare: Palpitations, chest pain, cardiac failure, myocardial infarction.
Vascular disorders:
Very rare: Hypertension, hypotension, vasculitis.
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal disorders:
Rare: Asthma (including dyspnoea).
Very rare: Pneumonitis.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Common: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, flatulence, anorexia.
Rare: Gastritis, gastrointestinal haemorrhage, haematemesis, haemorrhagic diarrhoea, melaena, gastrointestinal ulcer with or without bleeding or perforation (sometimes fatal particularly in the elderly).
Very rare: Colitis (including haemorrhagic colitis and exacerbation of ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease), constipation, stomatitis (including ulcerative stomatitis), glossitis, oesophageal disorder, diaphragm-like intestinal strictures, pancreatitis.
Hepatobiliary disorders:
Common: Increased Transaminases.
Rare: Hepatitis, jaundice, liver disorder.
Very rare: Fulminant hepatitis, hepatic necrosis, hepatic failure.
Skin and Subcutaneous tissue disorders:
Common: Rash.
Rare: Urticaria.
Very rare: Bullous eruptions, eczema, erythema, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome), dermatitis exfoliative, loss of hair, photosensitivity reaction, purpura, allergic purpura, pruritus.
Renal and Urinary disorders:
Very rare: Acute renal failure, haematuria, proteinuria, nephritic syndrome, interstitial nephritis, renal papillary necrosis.
General disorders and Administration site conditions:
Rare: Oedema.
Reproductive system and Breast disorders:
Very rare: Impotence.
Clinical trial and epidemiological data consistently point towards an increased risk of arterial thrombotic events (for example myocardial infarction or stroke) associated with the use of diclofenac, particularly at high doses (150 mg daily) and in long-term treatment.
Overdose
Symptoms:
There is no typical clinical picture resulting from diclofenac overdosage. Overdosage can cause symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, gastrointestinal bleeding, diarrhoea, dizziness, disorientation, excitation, coma, drowsiness, tinnitus, fainting or convulsions. In the case of significant poisoning, acute renal failure and liver damage are possible.
Therapeutic measures:
Management of acute poisoning with NSAIDs, including diclofenac, essentially consists of supportive measures and symptomatic treatment. Supportive measures and symptomatic treatment should be given for complications such as hypotension, renal failure, convulsions, gastrointestinal disorder, and respiratory depression.
Special measures such as forced diuresis, dialysis or haemo-perfusion are probably of no help in eliminating NSAIDs, including diclofenac, due to high protein binding and extensive metabolism.
Activated charcoal may be considered after ingestion of a potentially toxic overdose, and gastric decontamination (e.g. vomiting, gastric lavage) after ingestion of a potentially life threatening overdose.
Pharmacodynamic properties:
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs).
Mechanism of action:
EPIFENAC is a nonsteroidal agent with marked analgesic/anti- inflammatory properties. It is an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthetase, (cyclo-oxygenase).
Diclofenac sodium in vitro does not suppress proteoglycan biosynthesis in cartilage at concentrations equivalent to the concentrations reached in human beings.
There is limited clinical trial experience of the use of diclofenac in JRA/JIA paediatric patients.
Pharmacokinetic properties:
Absorption:
Tablets: Absorption is complete but onset is delayed until passage through the stomach, which may be affected by food which delays stomach emptying. The mean peak plasma diclofenac concentration reached at about 2 hours (50 mg dose produces 1.48 ± 0.65μg/ml (1.5μg/ml ≡ 5μmol/l)).
SR Tablets: The same amount of active substance is released and absorbed from SR tablets as from enteric-coated tablets. Mean peak plasma concentrations of diclofenac are reached at 4 hours, 0.508 ± 0.185 µg/ml (0.5 µg/mL Ξ 1.6 µmol/L) or 0.4 ± 0.184 µg/ml (0.4 µg/mL Ξ 1.25 µmol/l) after 100 mg or 75 mg SR Tablets, respectively. 75 mg and 100 mg SR Tablets are modified release preparations and plasma concentrations of diclofenac of 13 ng/mL (40 µmol/L) can be recorded at 24 hours (100 mg SR Tablets) and 16 hours (75 mg SR Tablets) after administration. Absorption is unaffected by food.
Bioavailability:
About half of the administered diclofenac is metabolised during its first passage through the liver ("first-pass" effect), the area under the concentrations curve (AUC) following oral administration is about half that following an equivalent parenteral dose.
Pharmacokinetic behaviour does not change on repeated administration. Accumulation does not occur, provided the recommended dosage intervals are observed. The plasma concentrations attained in children given equivalent doses (mg/kg, b.w.) are similar to those obtained in adults.
SR Tablets: The systemic availability of diclofenac from the SR formulations is on average, 82% of that achieved with the same dose of enteric-coated tablets (possibly due to release rate dependent first-pass metabolism). As a result of the slower release of active substance, peak plasma concentrations are lower than for the equivalent enteric-coated tablets.
Pharmacokinetic behaviour does not change on repeated administration. Accumulation does not occur, provided the recommended dosage intervals are observed. Through levels of diclofenac in the plasma after 100 mg SR daily or 75 mg SR twice daily are around 22 ng/ml or 25 ng/ml (70 nmol/l or 80 nmol/l), respectively.
Distribution:
The active substance is 99.7% protein bound, mainly to albumin (99.4%).
Diclofenac enters the synovial fluid, where maximum concentrations are measured 2-4 hours after the peak plasma values have been attained. The apparent half-life for elimination from the synovial fluid is 3-6 hours. Two hours after reaching the peak plasma values, concentrations of the active substance are already higher in the synovial fluid than they are in the plasma and remain higher for up to 12 hours.
Diclofenac was detected in a low concentration (100 ng/mL) in breast milk in one nursing mother.
The estimated amount ingested by an infant consuming breast milk is equivalent to a 0.03 mg/kg/day dose.
Metabolism:
Biotransformation of diclofenac takes place partly by glucuronidation of the intact molecule, but mainly by single and multiple hydroxylation and methoxylation, resulting in several phenolic metabolites, most of which are converted to glucuronide conjugates. Two phenolic metabolites are biologically active, but to a much lesser extent than diclofenac.
Elimination:
The total systemic clearance of diclofenac in plasma is 263 ± 56 mL/min (mean value ± SD). The terminal half-life in plasma is 1-2 hours. Four of the metabolites, including the two active ones, also have short plasma half-lives of 1-3 hours.
About 60% of the administered dose is excreted in the urine in the form of the glucuronide conjugate of the intact molecule and as metabolites, most of which are also converted to glucuronide conjugates. Less than 1% is excreted as unchanged substance. The rest of the dose is eliminated as metabolites through the bile in the faeces.
Characteristics in patients:
Elderly: No relevant age-dependent differences in the drug's absorption, metabolism, or excretion have been observed, other than the finding that in five elderly patients, a 15-minute I.V. infusion resulted in 50% higher plasma concentrations than expected with young healthy subjects.
Patients with renal impairment: In patients suffering from renal impairment, no accumulation of the unchanged active substance can be inferred from the single-dose kinetics when applying the usual dosage schedule. At a creatinine clearance of < 10 mL/min, the calculated steady-state plasma levels of the hydroxy metabolites are about 4 times higher than in normal subjects. However, the metabolites are ultimately cleared through the bile.
Patients with hepatic disease: In patients with chronic hepatitis or non-decompensated cirrhosis, the kinetics and metabolism of diclofenac are the same as in patients without liver disease.
Storage
Store in a dry place at a temperature not exceeding 30°C.
Packaging
EPIFENAC 25 mg Enteric coated Tablets: Box containing blisters of 10 enteric coated tablets each.
EPIFENAC 50 mg Enteric coated Tablets: Box containing 2 strips of 10 enteric coated tablets each.
EPIFENAC 75 mg SR Film coated Tablets: Box containing 1, 2, or 3 blisters each of 10 sustained release film coated tablets each.
EPIFENAC 100 mg SR Film coated Tablets: Box containing 1 blister of 10 sustained release film coated tablets.
Write a review
Your Name:Your Review: Note: HTML is not translated!
Rating: Bad Good
Enter the code in the box below: