- Anti-hestaminic & Respiratory Drugs (20)
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs (192) +-
- Baby & Mom (1281) +-
- Baby & Mom > Bath, skin & Hair > Skin Care > wibes (53)
- Beauty (2749) +-
- Beauty > Skin Care > whitening (273)
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response (860) +-
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response > ANTI-FUNGAL (11)
- Chemotherapy & Immune Response > Chemotherapeutic Agents > Hormone Antagonists >Enzyme Inhibitors (283)
- CIRCULATORY DISTURBANCE AGENTS (23)
- Diet & Fitness Products (276) +-
- DRUG AFFECTING CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (190)
- HEMATOLOGY (39)
-
Medical Supplies (496)
+-
- Chemicals & Disinfectants (19)
- Dental Supplies (26)
- Devices & Instruments (10)
- Diabetic Supplies (119)
- General Medical Supplies (21)
- I.V & Medical Solution (0)
- Intensive Care Unit & Anesthesia Supplies (0)
- KIDNEY UNIT SUPPLIES (21)
- Lab Supplies (3)
- Miscellaneous (21)
- Neonatal Unit Supplies (0)
- Operation Room Supplies (2)
- Sanitary (5)
- Sterilization Supplies (0)
- Surgical Sutures (4)
- Syringes (3)
-
Medicines & Health (2540)
+-
- Allergy & Sinus (94)
- Children's Health Care (51)
- Cough, Cold & Flu (273)
- Digestive Health & Nausea (224)
- Ear, Nose & Throat Care (177)
- Eye Care (116)
- Feminine Care (319)
- Foot Care (4)
- Orthopaedic Appliances (0)
- Pain Relief & Management (233)
- Pill Organizer (2)
- Skin Treatments (745)
- Sleep & Snoring Aids (2)
- Support & Braces (6)
- Medicines & health > Gout releif (42)
- Natural & Organic Products (82) +-
- OTC > Analgesics > Anti-inflammatory Drugs (45)
-
Personal Care (3083)
+-
- Bath & Body (256)
- Deodorant & Anti-perspirants (179)
- Ear, Nose & Throat Care (173)
- Eye Care (122)
- Feminine Care (366)
- Foot Care (12)
- Hair Care (411)
- Home Tests & Monitorings (14)
- Incontinence (7)
- Lip Care (21)
- Massage & Relaxation (18)
- Natural & Organic Personal Care (7)
- Oral Care (83)
- Pregnancy & Fertility (64)
- Shaving & Grooming (65)
- Sun Care (68)
-
Prescription Drugs (2820)
+-
- Analgesics (182)
- Cardiovascular System (369)
- Drugs Affecting Musculoskeletal System (64)
- Drugs Used In Infections (55)
- Ear & Nose Drugs (2)
- Endocrine System (173)
- Gastrointestinal Tract (238)
- Gastrointestinal Tract > Hepatology > Liver treatment (59)
- GYNECOLOGY (2)
- Miscellaneous (11)
- NEPHROLOGY > URINARY SYSTEM > RENAL DISORDERS > URINARY TRACT DISORDERS (46)
- NEUROLOGY (218)
- Nutrients & Blood Electrolytes (2)
- Respiratory System (150)
- SKIN > NAILS > HAIR > TOPICAL PREPARATIONS (46)
- Vaccines (1)
- Prescription drugs > Cardiovascular system > Anti-hypertension drugs (239)
- Sexual Wellness (298) +-
- Vitamins & Minerals Supplements (1175) +-
Ex Tax: 51EGP
Example
You can return the product within 14 days of purchase.
ReturnsYou can return the product within 14 days of purchase.

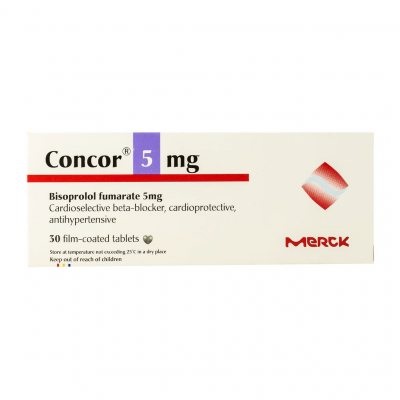
Concor ® 5 mg ( Bisoprolol ) 30 film-coated tablets
Product information (abbreviated prescribing information)
Products:
Concor 5, 10; Concor COR 1.25, 2.5, 3.75, 5, 7.5, 10 film-coated tablets for oral use
containing 1.25 mg, 2.5 mg, 3.75 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, or 10 mg bisoprolol fumarate,
respectively. Different brand names are used for the products in some countries.
Indications:
Concor: Treatment of hypertension; treatment of coronary heart disease (angina pectoris,
AP). Concor Cor: treatment of stable chronic moderate to severe heart failure in addition to
ACE inhibitors, and diuretics, and, optionally cardiac glycosides; treatment of stable chronic
heart failure (CHF).
Posology:
Treatment of hypertension or AP: the dosage is 5 mg bisoprolol fumarate once daily which
may be increased to 10 mg once daily if necessary. The max. recommended dose is 20 mg
once daily. Treatment of stable CHF: requires a titration phase, starting with a low dose (1.25
mg once daily) and with gradual up-titration (2.5, 3.75, 5, 7.5, 10 mg once daily) according to
tolerability It is recommended that the treating physician is experienced in the management
of CHF. The max. recommended dose for CHF is 10 mg bisoprolol fumarate once daily. The
treatment with bisoprolol must not be stopped abruptly, since this might lead to a transitory
worsening of condition, especially in patients with ischemic heart disease or CHF. Special
populations: In severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <20 ml/min) or severe liver
function disorders a daily dose of 10 mg bisoprolol fumarate should not be exceeded and
dose titration in patients with CHF and these functional impairments should be made with
particular caution. Use in children cannot be recommended (lack of experience).
Contraindications:
Acute heart failure or during episodes of heart failure decompensation, cardiogenic shock,
second or third degree AV block, sick sinus syndrome, sinoatrial block, symptomatic
bradycardia or hypotension, severe bronchial asthma, severe forms of peripheral arterial
occlusive disease or severe forms of Raynaud’s syndrome, untreated phaeochromocytoma,
metabolic acidosis, hypersensitivity to bisoprolol or to any of the excipients.
Warnings and precautions for use:
Cessation of therapy with bisoprolol must not be done abruptly unless clearly indicated,
transitional worsening of heart condition possible. AP/Hypertension: To be used with caution
with accompanying heart failure. CHF: To be initiated with a special titration phase. Initiation
of treatment of stable chronic heart failure with bisoprolol necessitates regular monitoring. No
therapeutic experience in CHF in patients with: insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (type I),
restrictive cardiomyopathy, congenital heart disease, haemodynamically significant organic
valvular disease, myocardial infarction within 3 months. CHF: No therap. experience in
patients with: NYHA class II heart failure, impaired renal (serum creatinine ≥ 300 micromol/l)
and liver function, older than 80 years.
All indications: Must be used with caution in: Diabetes mellitus showing large fluctuations in
blood glucose values, symptoms of hypoglycemia can be masked; strict fasting; ongoing
desensitisation therapy; first degree AV block; Prinzmetal’s angina; peripheral arterial
occlusive disease. Patients with psoriasis or with a history of psoriasis should only be given
beta-blockers (e.g. bisoprolol) after a careful balancing of benefits and risks. Symptoms of
thyrotoxicosis may be masked. In patients with phaeochromocytoma bisoprolol must not be
administered until after alpha-receptor blockade. In patients undergoing general anesthesia,
the anesthesist must be aware of beta-blockade. If it is thought necessary to withdraw betablocker therapy before surgery, this should be done gradually and completed about 48 hours
before anesthesia. Although cardioselective (beta1) beta-blockers may have less effect on
lung function than non-selective beta-blockers, as with all beta-blockers, these should be
avoided in patients with obstructive airways diseases, unless there are compelling clinical
reasons for their use. Where such reasons exist, Concor® / Concor® COR may be used with
caution. In bronchial asthma or other chronic obstructive airways diseases; concomitant
bronchodilating therapy is recommended. Increase of the airway resistance may occur in
patients with asthma, therefore the dose of beta2-stimulants may have to be increased. The
ability to drive a vehicle or to use machines may be impaired. This needs to be considered
particularly at start of treatment, upon change of medication, or in conjunction with alcohol.
Important Interactions:
Class I antiarrhythmic drugs, Calcium antagonists of the verapamil type and to a lesser
extend of the diltiazem type, Centrally-acting antihypertensive drugs.
Pregnancy and lactation:
Bisoprolol is not recommended during pregnancy and lactation.
Adverse reactions:
Very common: bradycardia.
Common: worsening of pre-existing heart failure, dizziness, headache, gastrointestinal
complaints such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, constipation; feeling of coldness or
numbness in the extremities, hypotension, asthenia, fatigue.
Uncommon: AV-conduction disturbances, worsening of pre-existing heart failure,
bradycardia, bronchospasm in patients with bronchial asthma or a history of obstructive
airway disease, muscle weakness, muscle cramps, asthenia, depression, sleep disorders.
Rare: increased triglycerides, increased liver enzymes (ALAT, ASAT), reduced tear flow,
hearing disorders, allergic rhinitis, hypersensitivity reactions such as itching, flush, rash;
hepatitis, potency disorders, nightmares, hallucinations.
Very rare: conjunctivitis, alopecia; beta-blockers may provoke or worsen psoriasis or induce
psoriasis-like rash.
Frequency not known: syncope.
Overdose:
The most common signs expected with overdose of a beta-blocker are bradycardia,
hypotension, bronchospasm, acute cardiac insufficiency and hypoglycaemia. There is a wide
inter-individual variation in sensitivity to one single high dose of bisoprolol and patients with
heart failure are probably very sensitive. If overdose occurs, discontinuation of bisoprolol
treatment and supportive and symptomatic treatment is recommended.
Marketing Authorisation Holder:
Merck Serono (a division of Merck KGaA, Frankfurter Str. 250, 64293 Darmstadt, Germany;
www.merckgroup.com)
Date of product information preparation:
July 2015
Please refer to local prescribing information as this may vary between countries.
Write a review
Your Name:Your Review: Note: HTML is not translated!
Rating: Bad Good
Enter the code in the box below: